Asset Risk Assessment - Vesta Finance
A risk assessment of Vesta Stable (VST) & Vesta Finance for Curve veCRV holders
Useful links
Abstract
Vesta Finance, a Layer 2-first lending protocol that issues an ERC20 USD-pegged stablecoin VST (Vesta Stable), has applied to add VST/FRAX Factory Pool to the Gauge Controller to enable users to assign gauge weight and mint CRV. Vesta Finance and Frax Finance submit the proposal to add VST/FRAX to the gauge controller. It is in Vesta and Frax’s interest to promote deep liquidity for VST and FRAX on Arbitrum in order to advance Arbitrum’s stablecoin ecosystem. In this post, we will explore the opportunities and risks that the Vesta Finance protocol offers and entails.
A TL;DR for people looking for a quick summary:
The proposal to add VST/FRAX is submitted jointly by Vesta Finance and Frax Finance to promote deeper liquidity for VST and FRAX on Arbitrum.
The Vesta Finance protocol is based on the battle-tested codebase of Liquity. However, there appear to have been changes made in the technical implementation.
Vesta Finance acknowledges that it is based on the mainnet-based borrowing protocol Liquity and is allocating 2% of the governance token VSTA to LQTY stakers.
Vesta V1's governance is conducted via Snapshot and decisions are manually approved by a 2-of-4 (After this article the Vesta Finance team updated the multisig to 3-of-4) multi-sig In a similar way to Barnbridge’s Genesis DAO, it will transition to community governance in the V2 phase.
The Vesta Contracts seem to be upgradeable this can result in a RUG!
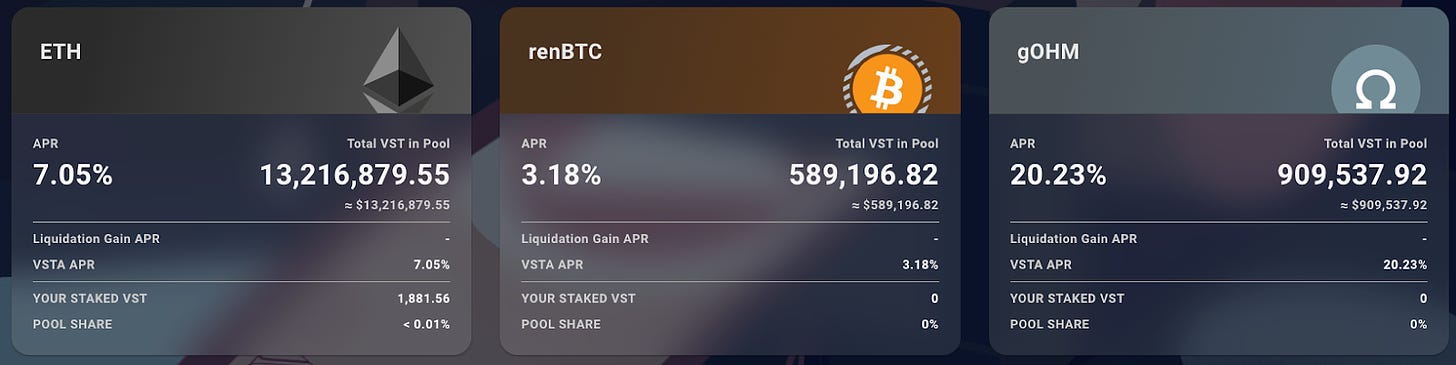
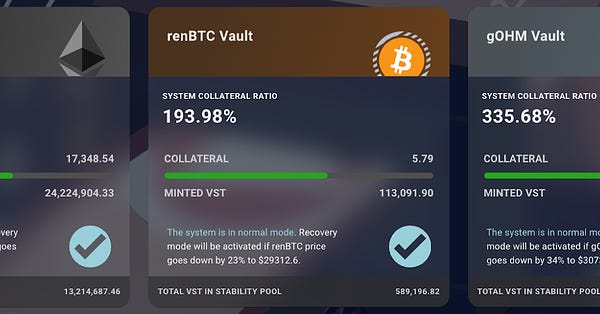
A variety of Vesta vaults are planned, starting with ETH, renBTC, and gOHM, with more to be added in the future. Each vault will have its own Stability pool.
When the total collateralization ratio (TCR) of the system falls below the critical collateralization ratio (CCR) for that collateral type, Recovery Mode is activated.
The Verilog Vesta Finance audit reveals only minor issues but it would be good to see more security audits to be done on Vesta Finance.
It is possible to RUG users since the Vesta Finance contracts are still upgradeable.
The project can not continue if the core team vanishes there is a big reliance still on the multisig that is controlled by the core team (After this article the Vesta Finance team updated the multisig to 3-of-4).
Vesta Finance & Vesta Stable (VST)
Vesta Finance is a Layer 2-first lending protocol that allows users to obtain maximum liquidity against their collateral without paying interest. It is based on the battle-tested codebase of Liquity. It is encouraging to see the Vesta Finance community working closely in collaboration with the Liquity team. The Vesta Team acknowledges that it is based on the mainnet-based borrowing protocol Liquity and is allocating 2% of the governance token VSTA to LQTY stakers. Vesta Finance has two different tokens: VST and VSTA.
VST is an ERC20 crypto-backed stablecoin minted by users when they deposit collateral. In the current, initial stages of the protocol, there are 3 types of collateral supported: ETH, renBTC, and gOHM. Over time, as Vesta ramps up its partnerships, this number will increase. As an L2-first project, it is also one of the first native lending protocols live on the Arbitrum mainnet. VST aspires to become one of the core stablecoins used for trading on L2s.
VSTA is an ERC20-based governance token. While it is currently not used in the governance process, the team is brainstorming on options for the future usage of VSTA: for example, long-term staking and weighted governance approaches(inspired by models like Curve’s veCRV). The protocol parameters (which would normally be set by LQTY stakers) are determined by a multisig approval process.
Vesta Finance is based on the open-source, Liquity codebase. It apparently has zero centralization vectors, zero potential for governance attacks, and is capable of surviving without a team. The (forked) code has been fully audited by the best of the best. We plan to explore this code in more detail to see how it was developed and if it contains any major changes.
Vesta VST price stability
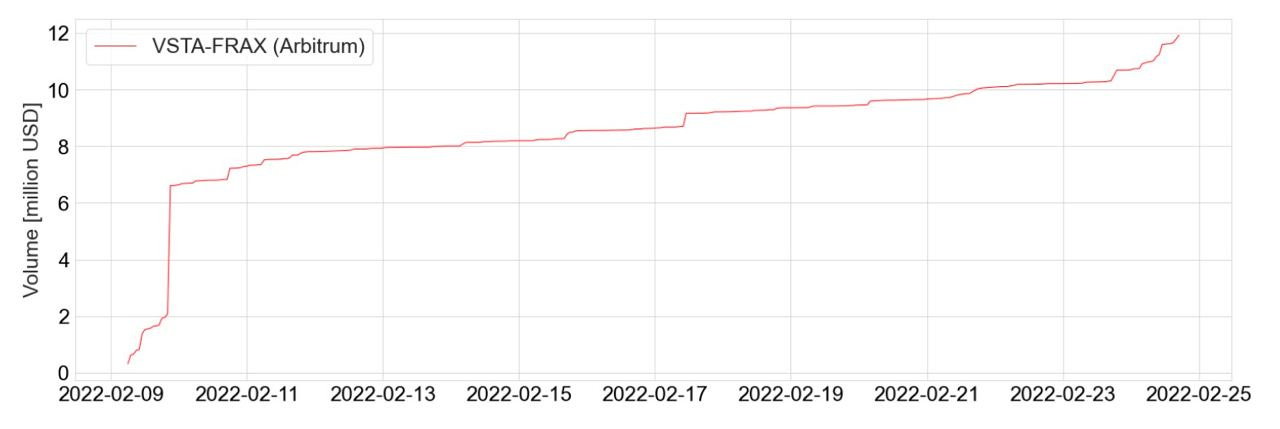
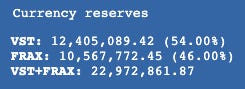
The VST USD-pegged stablecoin is an ERC20 token minted and issued by the users of the Vesta Protocol. As of the protocol launch, users were able to collateralize three types of collateral ETH, renBTC, and gOHM. The number of supported collaterals will increase over time as Vesta ramps up its partnership effort with other protocols in the Arbitrum ecosystem. Vesta is an L2-first project and has been one of the first native lending protocols live on the Arbitrum mainnet. VST aims to become one of the cornerstone stablecoins for trading on L2s. The Curve Factory pool VST+FRAX achieved a peak of $30M+- TVL and currently sits at $23M+- TVL. It is one of the deepest liquidity pools on Curve’s Arbitrum implementation.
VST’s price history is short but relatively stable for a newly-launched stablecoin, as can be seen on CoinGecko. Vesta’s redemption feature creates an effective price floor, as users can always redeem VST for the underlying collateral. Meanwhile, the collateralization ratio for the various assets classes serves as a price ceiling.
There are different Vesta vaults for different collateral types, beginning with ETH, renBTC, and gOHM. More collateral types will be added in the future. Each vault has its own liquidity pool. To force price stability Vesta utilizes a two-step liquidation mechanism in the following order of priority:
Replenishunder-collateralized vaults using VST tokens from the Stability Pool.
When / if the Stability Pool is empty, redistribute the under-collateralized vaults to other borrowers.
The Stability Pools of each vault contains a supply of VST tokens whose purpose is to “absorb” under-collateralized debt, i.e. to repay the liquidated borrower's liability. Stability Pool depositors are incentivized to stake their VST tokens for a yield that is generated by liquidations (i.e. through liquidation fees). When using B-Protocol, rebalancing of stability pools can be automated.
Recovery Mode
When the total collateralization ratio (TCR) of the system falls below the critical collateralization ratio (CCR) for a given collateral type, Recovery Mode is activated. Recovery Mode is structured to incentivize borrowers to behave in ways that push the collateralization ratio back above the CCR, and to incentivize (likely by high yields) VST holders to replenish the Stability Pool.
In economic terms, Recovery Mode is designed to encourage users to top up collateral and pay down debt. It also acts as a deterrent: the possibility of it occurring guides the system away from ever reaching it.
Vesta VST governance
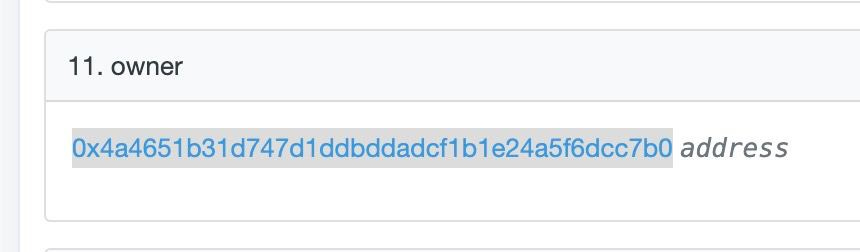
The VST token contract deployed by Vesta is currently “owned” by the Vesta governance 2-of-4 (After this article the Vesta Finance team updated the multisig to 3-of-4) multisig wallet on Arbitrum, found at 0x4A4651B31d747D1DdbDDADCF1b1E24a5f6dcc7b0.
The multisig consists of four individuals: 0xMaki, Darren Lau, Mikey Milken (Vesta Core Contributor), 0xAtum (Vesta Core Contributor). The current plan is to formalize the governance structure within weeks. Vesta V1's governance is conducted via Snapshot and decisions are approved manually via multi-sig, in a similar fashion to Barnbridge’s Genesis DAO. The protocol is intended to transition to full on-chain governance in V2 mode. Users will also be able to vote for parameter changes, which the protocol will execute automatically on-chain. The Genesis DAO multi-sig mechanism would, therefore no longer be needed to execute governance decisions. Below, you'll find parameters within the lending protocol that can be altered through governance procedures.
Liquidation Ratio
MCR: Minimum Collateral Ratio.
CCR: Critical Collateral Ratio / Minimum Collateral Ratio (in Recovery Mode).
Liquidation
MIN_NET_DEBT: The minimum amount of VST required to mint when first opening a vault.
PERCENT_DIVISOR: Liquidation Fee.
Opening/minting
BORROWING_FEE_FLOOR: The minimum fee amount for borrowing.
MAX_BORROWING_FEE: The maximum fee that can be charged for borrowing.
Redemption
REDEMPTION_FEE_FLOOR: The minimum fee amount for redemption.
Adding VST to Curve
The Curve Factory pool VST/FRAX reached a peak of $30M+- TVL and currently sits at $23M+- TVL. It is one of the deepest liquidity pools on Curve’s Arbitrum implementation. The volume can be seen below this will most likely increase when more collateral types are added. Once this has taken place and VST is fully incentivized, the token should be a fairly high-volume pair for Curve (and thus revenue-generating for veCRV holders). Because Vesta is a lending protocol and VST is generated for leverage loans, it will most likely be sold into the Curve pool for more leverage (similar to MIM) making the VST pairs both high-volume and high-turnover.
The Vesta team is staffed with DeFi veterans, with many strong advisors, including 0xMaki, DCF God, and Not3Lau Capital. These individuals will divert their CVX/CRV votes into the VST/FRAX pool in order to promote future incentivization. This will signal a commitment to the Convex/Curve community, and make the adding of the Vesta pools a net positive in volume growth and adoption for Curve. In addition to this, there are plans to incentivize Curve pools with VSTA incentives.
Security audits
Vesta’s current technical implementation is largely based on Liquity. However, when comparing the two protocols closely, we find there are changes in the technical implementation of Vesta, with over 114 altered files. This has to be taken into account: while Liquidity is battle-tested and robustly audited (see here), this is not yet the case for Vesta.
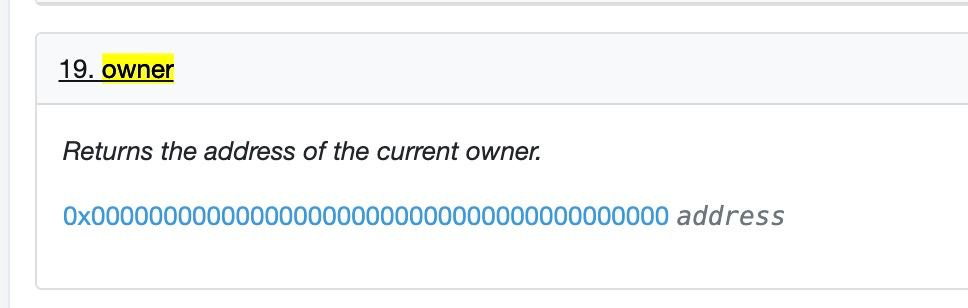
It also seems that Vesta has upgradable contracts with no time lock implemented this is dangerous and could result in a RUG! For example in BorrowerOperations.sol: the adjustTrove is one of the most important external functions. this one can adjust collateral among other things in Liquity we can see there is no owner of this contract and if we look in Vesta Finance it’s contract we can see that there is an owner.
Vesta has so far submitted to one audit by Verilog, a boutique smart contract security firm. A follow-up audit by Trail of Bits is planned for 2022 Q3 (the earliest possible timeslot for the auditors). In terms of oracle security, Vesta uses Chainlink feeds to obtain price data for the various collateral assets, and aims to create additional pools besides VST-FRAX further down the line so that eventually there can be a Chainlink oracle for VST itself.
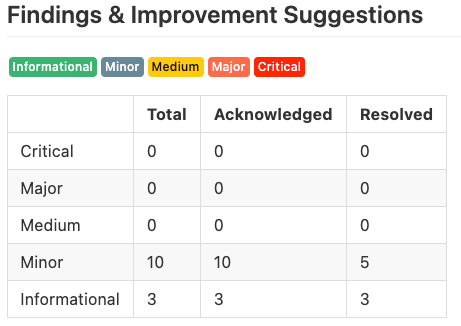
Zooming into the Verilog audit, we can find a system overview of the Vesta protocol and can review the core contracts. The audit findings identify only 10 minor issues (of which 5 were resolved by the end of the audit), together with 3 “informational findings/suggestions”. What is somewhat concerning is the absence of an official source of information about the company Verilog, or even an official Twitter account. According to a reference in a separate whitepaper, the firm is based in Vancouver, consisting of academics associated with the University of British Columbia. The founder, Zehua Wang, is an adjunct professor at UBC and has a background in computer and software engineering (view his profile here). From our perspective, one obvious improvement would be to increase the number of required signers for multisig approval currently 2-of-4 (After this article the Vesta Finance team updated the multisig to 3-of-4).
Conclusion: Vesta Finance
All things considered, Vesta Finance is in intriguing and elegant implementation of the Liquidy protocol. When the VST token is fully incentivized and more collateral types have been added, VST has potential as a fairly high-volume pair on Curve, and thus a source of revenue for veCRV holders. Since Vesta is a lending protocol, as VST is generated for leverage loans it will most likely be sold into Curve pools for more leverage (similar to MIM), making the VST pairs high turnover and high-volume.
Vesta Finance’s core logic and architecture are based on Liquity; although there are multiple changes Trail of Bits audit planned for Q3 2022 will hopefully give more clarity on this topic.
The audit by Verilog, a relatively small and unknown audit firm, revealed a positive picture with only minor issues discovered. The 2-of-4 (After this article the Vesta Finance team updated the multisig to 3-of-4) multisig could be more secure. One big concern is that the contract seems to be upgradable with no time lock implemented; this is dangerous and could result in a RUG!
The segregated vaults and stability pools with a fallback mechanism (i.e., redistributing to under-collateralized vaults) are points of uniqueness and give it the potential to become a core building block in the DeFi ecosystem as a landing protocol.
It would perhaps be worthwhile to onboard VST and the Vesta Finance community to a Curve Gauge and see what kind of interesting synergies can be built. With all this, we should keep in mind that Vesta Finance is a young protocol and has not yet been stress-tested in the field.
Does the asset meet minimum requirements?
Is it possible for a single entity to rug the user base?
Yes. Vaults and stability pools cannot be rugged by the Vesta Finance team. However, there are still only 2 out of 4 (After this article the Vesta Finance team updated the multisig to 3-of-4) multisig requirements (with 2 core members) to alter protocol parameters and perform an economic attack in favor of the core team. Looking at the platform’s endorsements and backers, such an attack seems unlikely. the contracts seem to be upgradable with no time lock implemented this is dangerous and could result in a RUG!
If the team vanishes, can the project continue?
No. The current Vesta Finance V1 implementation still relies on the core team to alter parameters and is on its pad towards full decentralization. There is however a clear path towards a fully decentralized V2 that will come out when the VSTA token economics and governance will be fully implemented.
Do the audits reveal any items of concern?
Yes. Vesta’s current technical implementation is largely based on Liquity, but close inspection reveals extensive changes. This has to be taken into account: whereas Liquidity is battle-tested and robustly audited, this is not jet the case for Vesta.
Recommendation: The risk assessment committee recommends that the Vesta Finance VST/FRAX pool to-be approved for a Gauge and that V2 be implemented before applying for more Gauges.
Follow me on Twitter and share this information to inform and educate more people.








Read was 2x what it needed to be because of the padding.
Also, the argument that the protocol being controlled by crypto personalities means the risks associated with a 2/4 multisig, manual parameter management, upgradeable contracts and audit by unknowns can be waved away is questionable at best.